The journey of the gas laser started with the helium-neon laser in 1960. People used it in many applications, but it was not enough. In 1964, the invention of CO2 laser revolutionized the field of laser technology. At present, the CO2 laser is one of the most powerful devices used in a wide range of cutting and engraving tasks.
This blog explores CO2 laser engraving, how it works, and its typical pros and cons. It also highlights how CO2 lasers differ from other types of laser engravers.
Part 1. What Is a CO2 Laser Engraver?
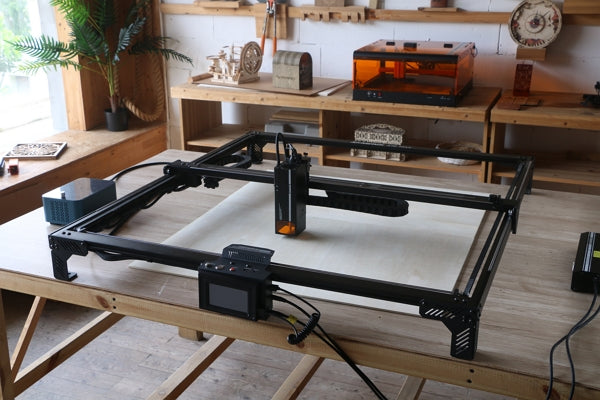
A CO2 laser engraver uses a CO2 laser beam to engrave or cut various materials. The highly focused laser can accurately engrave any design, text, or photo on almost all materials. Using this device, you can make a wide range of products. Custom signage, jewelry, personalized gifts, and decorative items are typical in this case.
A CO2 laser engraver is highly accurate. Various experts confirmed this device can achieve tolerances of up to ±0.05 mm to ±0.1 mm.
A CO2 laser engraving machine may have various specifications. The laser power may range from a few watts to several kilowatts. The power rating typically depends on the type and thickness of the material.
Part 2. How Does a CO2 Laser Engraver Work?
A CO2 laser engraving machine uses CO2 gas lasers to cut or engrave materials. The process starts by generating a CO2 laser from a gas mixture tube.

The gas mixture tube generally consists of CO2, helium, and nitrogen. When electricity passes through this tube, these gases become excited. During excitation, each molecule produces a laser beam. The CO2 laser beam is invisible to human eyes. Its wavelength is 10.6 micrometers.
Once the laser beams are produced, they travel through a series of mirrors. Finally, these laser beams are focused using a plano-convex lens. In this case, a plano-convex lens concentrates the laser beam into a fine point, known as the focal point.
The concentrated laser beam finally hits the material surface and begins engraving. When the laser beam hits the target area, it causes a rapid temperature rise. This heat typically causes the material to burn, melt, and vaporize away. This way, the CO2 laser engraver creates a tiny trench along the design path.
Part 3. Differences Between CO2 Laser and Other Laser
A CO2 laser engraver differs from fiber or diode laser engravers in various ways. Each point is critical when deciding on a suitable method for your project.
1. Laser Source
A CO2 laser engraving machine produces laser beams from a gas mixture tube, typically including CO2, N2, and helium. Depending on the application, other gases like hydrogen, xenon, and water vapor may also be present in this mixture.
On the other hand, fiber lasers come from doping with rare earth metals. The use of fiber optic cables is the reason behind the name "fiber laser." However, diode lasers are produced from semiconductor diodes.

2. Wavelength and Material Compatibility
CO2 lasers have a wavelength of about 10.6 micrometers. This wavelength is ideal for cutting and engraving non-metals.
On the other hand, fiber lasers have wavelengths ranging from 0.78 micrometers to 2.2 micrometers. This shorter wavelength is typically suitable for cutting and engraving metals.

Finally, diode lasers have wavelengths of 0.8 to 1 micrometer. They are typically versatile, but people mainly use them on wood, plastics, and other soft materials.
Human eyes usually can detect wavelengths roughly between 380nm to 700nm or 0.38 um to 0.7 um. All three lasers are typically invisible to human eyes.
3. Laser Speed
Fiber and diode lasers both have shorter laser wavelengths. Because of this, they offer faster cutting and engraving results. However, diode lasers often have less power.
In contrast, CO2 lasers have larger wavelengths, which take time for materials to absorb. Consequently, the cutting and engraving processes are also slow.
4. Maintenance
A CO2 laser engraver has a gas mixture tube that needs frequent replacement. Typically, a gas mixing tube has a service life of up to 12,000 hours. Besides, CO2 laser engravers also need maintenance for mirror alignment and cleaning lenses. Thus, the CO2 laser engraving machine needs more maintenance.

On the other hand, fiber and diode lasers need no consumables. They also don't need mirror alignment. Therefore, these laser engravers need less maintenance.
5. Cost
The initial cost of a CO2 laser engraving machine is lower. However, it needs consumables and maintenance, which increases the operational costs.
Fiber lasers typically have higher purchase costs. They need no consumables and require less maintenance. Therefore, the operating cost of these laser engravers is also lower.
A diode laser engraving machine offers low initial and operating costs. However, it typically has lower power systems.
Part 4. Can CO2 Laser Engrave Metal?
A CO2 laser engraver is a powerful tool, but when it comes to metal, it shows some limitations. As you know, the wavelength of CO2 lasers is 10.6 micrometers, which bare metals cannot absorb. Instead, they reflect it. Thus, CO2 lasers are not suitable for cutting bare metals. However, CO2 lasers can engrave metals only if they have a coating, like anodizing or powder coating.

Part 5. Advantages & Disadvantages of CO2 Laser Engraver
Advantages of CO2 Laser Engraver
The CO2 laser wavelength is typically larger than fiber, UV, and diode lasers. This unique feature usually offers a few benefits. Some of the key benefits are as follows:
- High Precision and Detail: CO2 laser engravers provide detailed and precise engravings. You can engrave intricate designs, text, logos, and even pictures. You can achieve tolerances of up to ±0.05 mm to ±0.1 mm.
- Fast Engraving Speed: Compared to other engraving methods, CO2 laser engraving is faster. Because of this, you can get high productivity in your project, making it suitable for large-scale production.
- Versatility with Non-metal Materials: The CO2 Laser engraver can work with all materials except bare metals. You can engrave or mark text or designs on wood, plastic, acrylic, leather, glass, and coated metals.
- Lower Upfront Cost: Compared to fiber lasers, CO2 lasers generally require low upfront costs. Because of this, CO2 laser engravers are more accessible to many businesses with tight budgets.
- Long Service Life: The gas laser mixing tube typically has a service life of up to 12,000 hours. If you run your device for 8 hours daily, you can use your machine before the first replacement in 3 years.
Disadvantages of CO2 Laser Engraving Machine
Although a CO2 laser engraving machine offers many advantages, it has some limitations.
- Limited Metal Engraving Capability: CO2 laser engraving machines produce lasers with larger wavelengths. These lasers typically reflect on the metal's surface, so the metal part can not fully absorb them. Therefore, the CO2 laser is not suitable for cutting or engraving metals.
- Higher Maintenance Needs: A CO2 laser engraver typically requires more maintenance than other laser engravers. Laser tubes, mirrors, and lenses normally need regular cleaning, and the gas mixing tube may need occasional replacement.
- High Operating Cost: A CO2 laser engraver needs a gas mixing tube to produce laser beams. You may occasionally need to replace this part. It increases the operation cost.
- Bulkier and Heavier: CO2 laser engravers can typically handle large parts and materials. Although this might suit particular applications, it makes the machine bulkier and heavier.
Part 6. What to Look for When Buying a CO2 Laser Engraver?
When buying a CO2 laser engraver, consider a few factors to choose the best fit for your project.
Laser Power Selection
Choose the laser power based on your intended use. Laser power from 20W to 60W is typically suitable for average engraving work. On the other hand, laser power ranging from 80W and above is ideal for cutting work.
Working Area Size
Another crucial factor is the working area. You can choose a working area that best fits the size of your project. A larger working area can handle many smaller items at a time.
Software Compatibility
Check the system's software compatibility. Does it support various file formats? Is the software easy to use? Modern laser engravers support popular software like LightBurn or EZCAD.
Cooling System
The next thing to look at is the cooling system. It significantly impacts the longevity of your CO2 laser engraving machine. You might have two options: a water chiller or an air cooler. A water chiller is more effective than an air cooling mechanism, especially for CO2 laser engravers.
Customer Support
Customer support is often crucial in choosing a suitable CO2 laser engraver. Try to find out how responsive the manufacturer's customer service team is. If you are a beginner, you may frequently need their help.
Cost Performance
Finally, compare the machine's cost to its performance. Check whether the pricing is reasonable for the specifications provided.
Final Words
We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights and a comprehensive understanding of CO2 laser engravers.
A CO2 laser engraver is a versatile solution for many applications. It is particularly suitable for non-metallic materials and can accomplish many projects. Renowned for its tight tolerances, a CO2 laser engraver can create a design with fine detail and produce a premium-quality product.
When selecting a CO2 laser engraver, consider key factors such as laser power and working area to ensure it meets your specific needs.